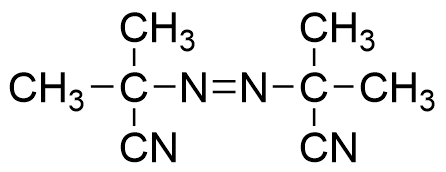
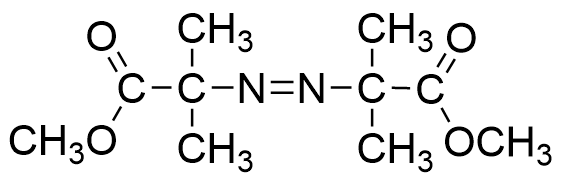
V-601
CAS : 2589-57-3


Plastics manufacturing
Photocurable
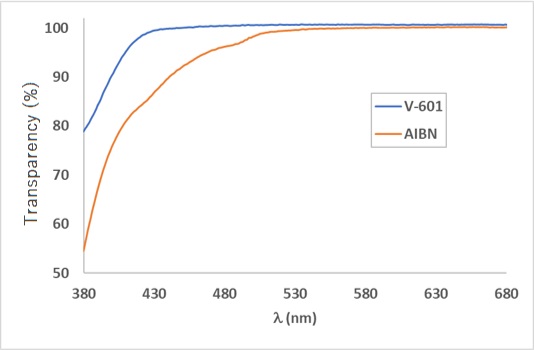
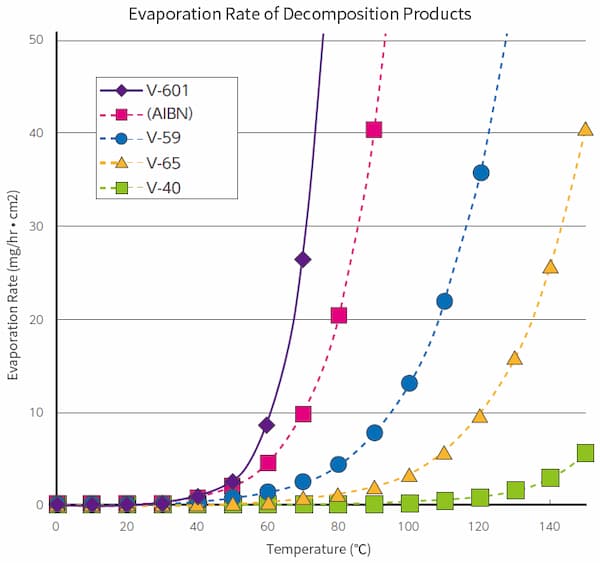
V-601 is a nitrile-free oil-soluble azo polymerization initiator which has similar level of polymerization activity as AIBN. A safer developed as alternative to AIBN, V-601 decomposition results in much less toxic byproducts. As a nitrile-free azo initiator, V-601 displays excellent solubility characteristics in organic solvents. Since the volatility of the decomposition product is higher than that of others, such a product can be removed in the process of polymer manufacturing. Being of non-nitrile type, the polymerized polymers are highly transparent, therefore, semiconductors and LCDs applications are expected.
- Non-nitrile azo initiator as an alternative to AIBN
- Freely soluble in various organic solvents, available for high solid coating.
- With equivalent polymerization activity of AIBN. Efficiency of polymerization rises in alcohol solvents
- 10 Hour half-life decomposition temperature: 66℃
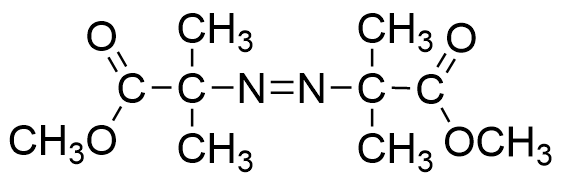
| Chemical name | Dimethyl 2,2'-azobis(2-methylpropionate) |
|---|---|
| CAS RN® | 2589-57-3 |
| Molecular weight | 230.26 |
| Molecular formula | C10H18N2O4 |
| Synonyms | Dimethyl 2,2'-azobisisobutyrate; MAIB 2,2'-Azobis(isobutyric acid methyl); AIBME |
Physical characteristics
| Color Appearance |
slightly yellow or light yellow crystals or oily liquid |
|---|---|
| Melting point/freezing point | 22-28℃ |
| 10hour half-life decomposition temperature | 66℃(in toluene) |
| Activation energy | 131.2 kJ/mol |
| Frequency factor (ln A) | 35.67 |
| Solubilities | water : insoluble. |
| SADT | 35℃ |
*SADT: Self-accelerating decomposition temperature
Packaging & Storage conditions
| Packaging | 10kg / 500g |
|---|---|
| Storage conditions | keep under 10℃ |
Related laws and regulations
| TSCA | Listed under 5e Consent Order |
|---|---|
| EINECS | Listed |
| REACH | 01-2120807902-57-0000 |