Lithium-ion rechargeable battery is currently used in mobile phones and so on. Further, it is expected to be a key component of automobiles and large-scale energy storage facilities. Therefore, it is required to control the interface between electrode and electrolyte. We have developed the material that forms a film on the interface between electrode and electrolyte, which results in a stable charge and discharge.
Performance improvement on lithium-ion rechargeable batteries
The capacity of lithium-ion rechargeable battery degrades gradually due to the decomposition of electrolyte on the surface of cathode/anode caused by repeating the cycle of charge/discharge.
On the other hand, to control the decomposition of electrolyte is attempted by adding various additive agents such as organic compound.
Especially, the additive agent which can control the reductive decomposition of the solvent by forming the stable film on anode by initial charge/discharge is required.
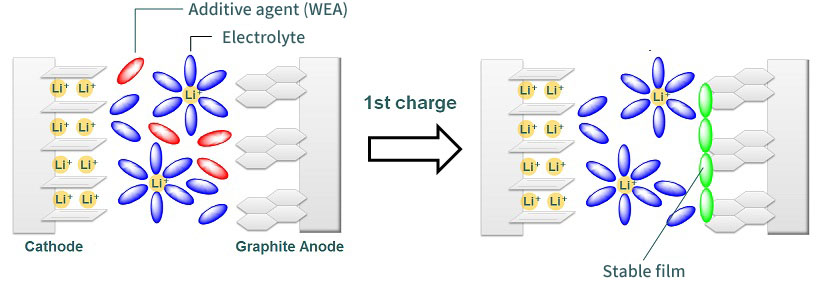
Characteristics of additives for lithium-ion rechargeable batteries
・Forms the stable film on the surface between electrode and electrolyte by the reductive decomposition.
・Controls the decomposition of electrolyte with the formed film and charges/discharges stably.
・Charges/Discharges quickly because lithium can transfer to the formed film smoothly.
Effect of additive agent
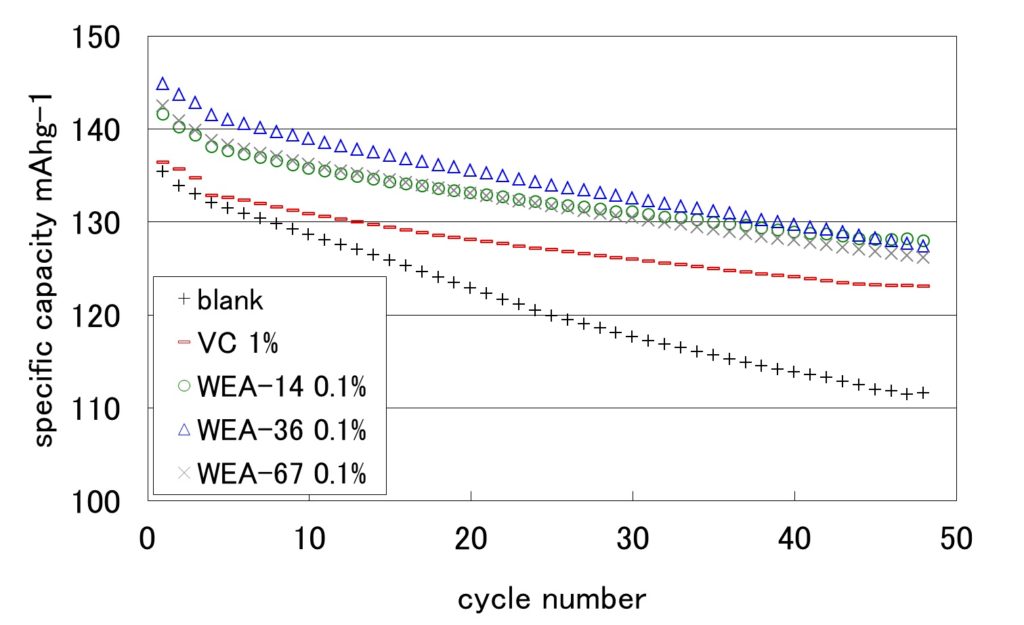
The horizontal axis shows the cycle number, and the vertical axis shows the discharge capacity. The capacity degrades as the cycle number increases in the case of no additive agent. In comparison, with 0.1% addition of vinylene carbonate, the initial capacity improves and the capacity degradation due to the cycle advance decreases in the case of WEA series. This result indicates that the capacity is improved by forming the film on the surface of electrode because the WEA series is designed to perform the reductive decomposition easily.

