RAFT Agents
Living Radical Polymerization,Chain Transfer Agents
RAFT polymerization is a technique that uses chain transfer agents (RAFT agents) to synthesize high-function polymers such as polymers with a narrow molecular weight distribution and block polymers. By combining the our company’s azo initiators and RAFT agents, precise polymerization reaction can be achieved only by adding them to an existing polymerization system. In our company, we offer RAFT agents that can be provided for mass production.
Characteristics of RAFT agents by FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
- 1. Production for safety and securityThere is no concern about lead time, supply capacity, quality variation, etc.
- 2. Product form that is easy to handleProducts with properties such as low odor and powder are also available, and they can be sold in various packaging forms.
- 3. Support for a wide range of quantitiesWe can provide in quantities from reagent scale to commercial scale.
- 4. Advanced synthesis and mass production technologyWe have records of synthesizing more than 500 functional compounds per year.
Items that can be provided for mass production
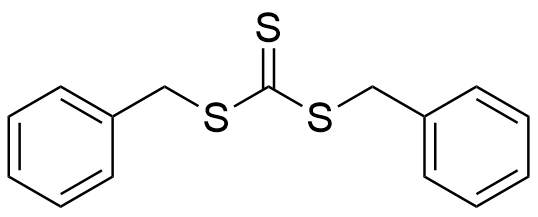
RAFT-011
CAS RN® : 26504-29-0
- Both-terminal extension type
- Applicable to styrene, acrylate, etc.
 View
View
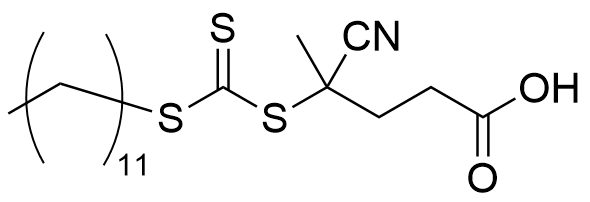
RAFT-013
CAS RN® : 870196-80-8
- One-terminal extension type
- Applicable to acrylate, methacrylate, etc.
 View
View
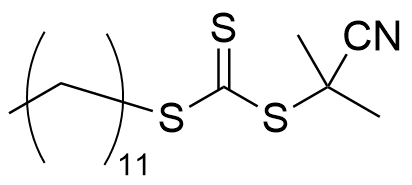
RAFT-009
CAS RN® : 870196-83-1
- One-terminal extension type
- Applicable to acrylate, methacrylate, etc.
 View
View
In addition to the above, our company is working on mass production of compounds that can be manufactured industrially from among our library of RAFT reagents. Please feel free to make an inquiry. Please feel free to contact our company if you wish to use RAFT agents, or if you have trouble securing a bulk source after examination.
Related items
Oil soluble Azo intiators
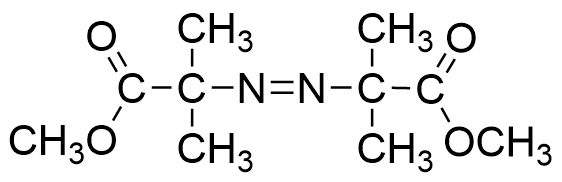
V-601
- Non-nitrile azo initiator as an alternative to AIBN
- With equivalent polymerization activity of AIBN. Efficiency of polymerization rises in alcohol solvents
- 10 Hour half-life decomposition temperature: 66℃
 View
View
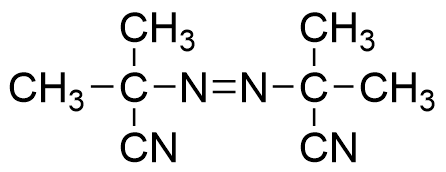
AIBN
- The most common azo initiator
- 10 Hour half-life decomposition temperature: 65℃
 View
View



