Special crosslinking agents

Plastics manufacturing
Photocurable
We have developed a unique crosslinking agent containing a bifunctional vinyl sulfonyl group.
Characteristics
1. Water-soluble: designed for use in water-based compositions
- In many applications the use of organic solvents is undesirable, and water-based systems are becoming more prevalent.
2. Two types of polymerizations
- Radical polymerization
The vinyl sulfonyl group can be polymerized radically,with compounds such as acrylates - Anionic polymerization
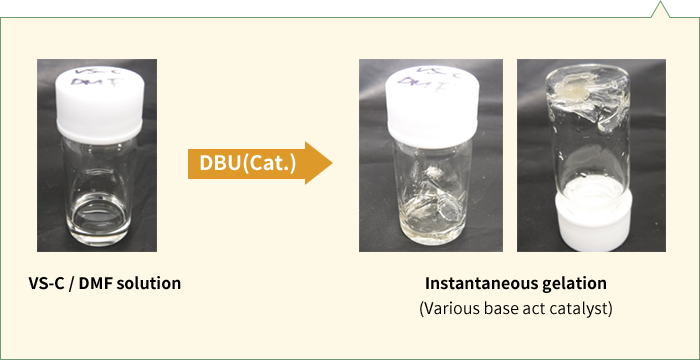
The compound independently polymerizes if there are base catalysts such as amines present. Since its reaction speed is lower than that of radical polymerization, the polymerization rate can be controlled by changing the polymerization temperature. Inactivation rarely occurs because this curing method causes no oxygen inhibition.
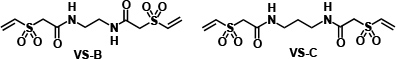
VS-B
C10H16N2O6S2
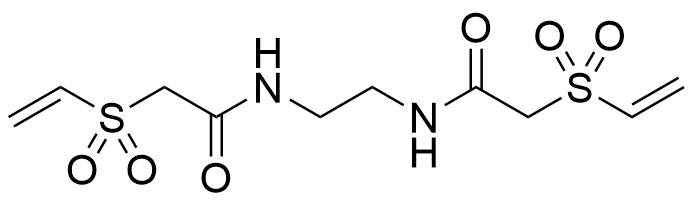
| Chemical name | N,N'- Ethylenebis [2-(vinylsulfonyl) acetamide] |
|---|---|
| CAS RN® | 66710-66-5 |
| Molecular weight | 324.37 |
Physical characteristics
| Appearance | White ~ light yellow granule |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 160-164℃ |
| Soluble solvent | DMF, NMP |
| Water-solubility | 10℃ 0.5wt% 20℃ 1wt% 30℃ 1.5wt% |
Related laws and regulations
| TSCA | Not Listed |
|---|---|
| EINECS | Listed |
| REACH | Not Listed |
VS-C
C11H18N2O6S2
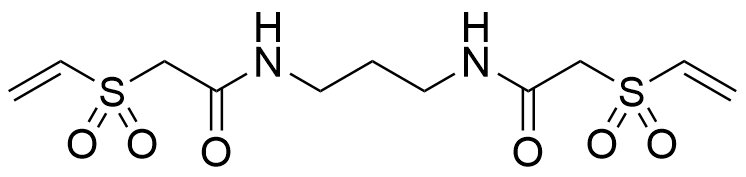
| Chemical name | N,N'- Trimethylenebis [2-(vinylsulfonyl) acetamide] |
|---|---|
| CAS RN® | 93629-90-4 |
| Molecular weight | 338.4 |
Physical characteristics
| Appearance | White ~ light yellow granule |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 106-108℃ |
| Soluble solvent | Water, DMF, NMP |
| Water-solubility | 10℃ 3wt% 20℃ 6wt% 30℃ 9wt% |
Related laws and regulations
| TSCA | Not Listed |
|---|---|
| EINECS | Listed |
| REACH | Not Listed |
Performance comparison
| Vinylsulfone Compound | Radical polymerization |
Water solubility |
Curing with catalytic amount of base |
|---|---|---|---|
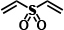 |
Yes | Non | Non |
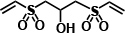 |
Yes | Yes | Non |
 |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
Example 1: UV-radical curing (water-based)
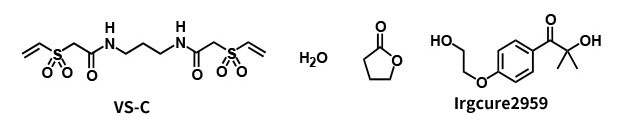
Procedure
- Mix 100 parts of VS-C (Product of FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation), 50 parts of H2O and 100 parts of γ-butyrolactone, and dissolve by heating to 100℃.
- Add 5 parts of photoradical initiator.
- Apply it to glass substrate. (Evaporate at 120℃ for 1 minute)
- Irradiate with UV-LED for 5 seconds. (100mW/cm2 (365nm)) → Cured film is formed at room temperature.
- UV-cured film is insoluble in the organic solvents such as water, acetone, methanol and so on.
- Environmental load can be reduced because water is used as the solvent.
- Unexposed area is developable with water.
Example 2: UV-radical and anionic curing
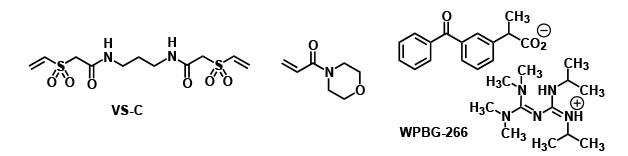
Procedure
- Mix 25 parts of VS-C (Product of FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation) and 100 parts of 4-acryloyl morpholine (Product of FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation), and dissolve completely by heating.
- Add 2.5 parts of WPBG-266 (Product of FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation).
- Apply it to glass substrate.
- Irradiate with UV-LED for 10 seconds. (100mW/cm2 (365nm))
- (As necessary) Heat at 100℃ for 1 to 10 minute(s).*
- *If shaded or dark part remains uncured due to no radical polymerization or if there remains tackiness on the surface due to polymerization inhibition by oxygen, they become cured by heating at 100℃ for 1 to 10 minute(s).
Contact us for more details.
We are waiting for questions and requests on products.

