RAFT-013
RAFT agent for mass production
This is a one-terminal reaction type RAFT agent that is suited to the polymerization of methacrylate. It can also be used for polymerization of styrene and acrylate.
- One-terminal extension type
- Applicable to acrylate, methacrylate, etc.
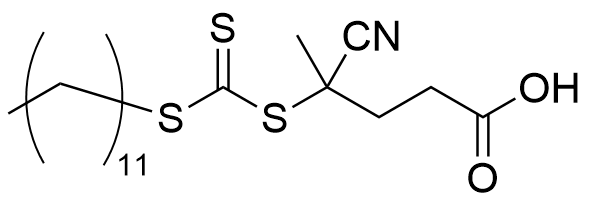
| Chemical name | 4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| CAS RN® | 870196-80-8 |
| Molecular weight | 403.67 |
Physical properties
| Appearance | Pale yellow - brown,crystalline powder - powder |
|---|---|
| Odor | Slightly sulfur odor |
| Melting point | 64~68℃ |
| Solubility |
Ethanol, acetone, PGME, PGMEA: Soluble Water, hexane: Insoluble |
Storage conditions
| Storage conditions | Store away from sunlight in well-ventilated place at room temperature(preferably cool) |
|---|
Monomer compatibility
Styrene〇
Acrylate〇
Acrylamide〇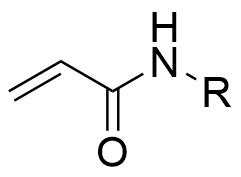
Methacrylate〇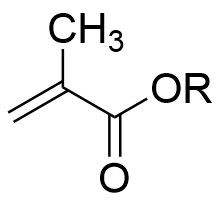
Methacrylamide〇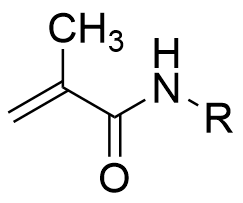
Vinyl ester×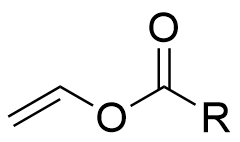
Vinylamide×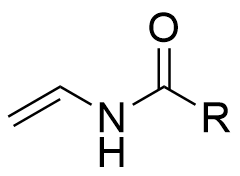
Related items
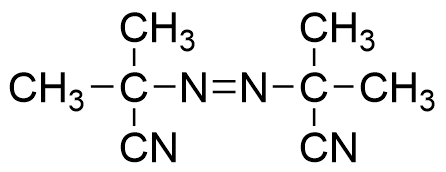
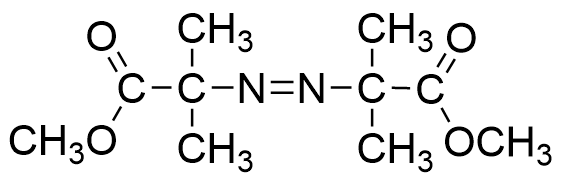
V-601
- Non-nitrile azo initiator as an alternative to AIBN
- With equivalent polymerization activity of AIBN. Efficiency of polymerization rises in alcohol solvents
- 10 Hour half-life decomposition temperature: 66℃
 View
View
Contact us for more details.
We are waiting for questions and requests on products.